User Tools
Sidebar
This is an old revision of the document!
JFFS
The JFFS menu contains settings and information used to create, prepare and view the status of a JFFS2 partition used for permanent storage.
Common routers contain two types of permanent storage:
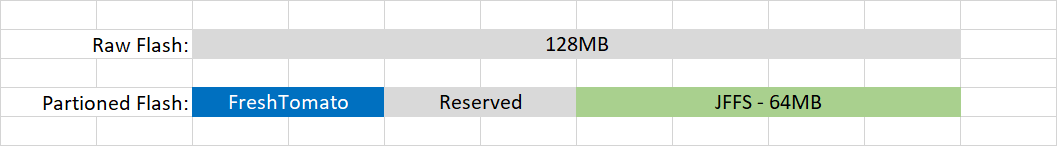
Flash - is the storage area where the FreshTomato firmware image is uploaded, stored and executed. At boot time, the image is loaded into a squash filesystem which means it's executed read-only. Flash size is measured in Megabytes (MB). You might find Flash storage occasionally referred to as Flash RAM. However, the FreshTomato team intentionally avoided this term, to reduce the chance of confusion with traditional (dynamic) RAM.
NVRAM - (Non-volatile RAM) is used for storing the hardware's configuration. While loading the firmware from the squash filesystem, parameters in the form of variables are fetched from the NVRAM. NVRAM size is relatively small and is measured in Kilobytes (KB).
Since modern routers have a relatively large amount of Flash memory available, FreshTomato can mount the unused storage space and make it available to FreshTomato's underlying (Linux) OS1) for normal file storage. This function is called JFFS, short for the Journalling Flash File System type used for the storage. Currently, JFFS2 (version 2) is used.
The figures below represent an example of storage allocation (not to scale). The numbers will vary based on your FreshTomato version and your hardware specifications. See the Hardware Compatibility page for more information on specific FLASH and NVRAM specifications.
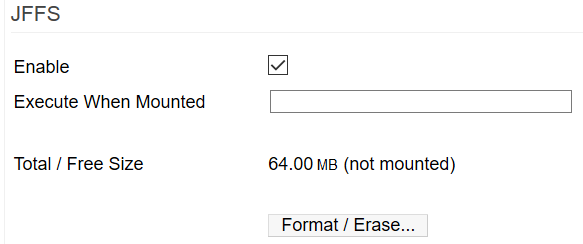
Enable: Checking this box enables JFFS, as shown in the image below. (Default: Disabled).
Execute when mounted: In this field, you can enter the name of a script or similar to run immediately after the partition becomes available to FreshTomato. (Default: blank).
Total / Free Size: This displays the storage size available to be used. This cannot be changed.
Format / Erase: The very first time you enable JFFS, you must format the partition with the JFFS2 filesystem. Once formatting is complete, the “(not mounted)” status should change to “(mounted)” to reflect that FreshTomato has access to the partition. Once the JFFS partition is mounted, it can be accessed in the filesystem under the root folder2) as /jffs .
NOTE: As a safety precaution, FreshTomato will prevent you from performing firmware upgrades if a JFFS partition is mounted/in use. The reason for this is that if you were to disable JFFS and upgrade the FreshTomato firmware, you might lose the contents of the /jffs partition. For this reason, you should do a backup and restore operation to preserve the data there. To learn more about backup and restore of JFFS partition data, see the XXXX page.
Notes/Troubleshooting
IMPORTANT: Flash storage is not designed for frequent write operations. Because of this, you should avoid performing frequent write operations to it. For example, avoid storing the logs in JFFS, as this will shorten the life of your router. However, flash memory's limitation is in the number or write operations, but not the number of read operations. Therefore, an Entware installation would be fine. Be aware that your JFFS should be used only if no other storage like USB or a CIFS share is available.