User Tools
Sidebar
This is an old revision of the document!
Firewall
The Firewall page allows you to configure options to protect/facilitate certain network communications.
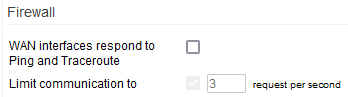
WAN interfaces respond to ping and traceroute - When enabled, this allows your device will reply to certain ICMP/UDP packets so that ping and traceroute from Internet hosts will work.
Limit communication to - Specifies the maximum number of requests per second to which the Firewall will reply. Setting a limit number is recommended to prevent DDoS attacks.
Enable TCP SYN cookies - Enabling this protects the router from SYN Flood attacks via a well-known technique called “SYN cookies”. This technique encodes info from the SYN packet into the response (SYN/ACK). Despite being a standard technique, enabling this will create some secondary limitations that my not be well-handled by some old TCP/IP stacks.
Enable DCSP Fix - This enables a workaround for a well-known issue related to DSCP (packet marking) when connected to the Comcast ISP.
IPv6 IPSec Passthrough -
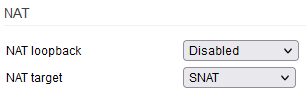
NAT loopback - also known as “Hairpinning”, this technique allows LAN devices to access another LAN device via the WAN interface of your router. This is common practice, for example when connecting to the DDNS domain of your router from the LAN (for administration purposes). This legacy setting is rarely, if ever needed nowadays Also, this function can create a bottleneck on fast connections.
- All
- Forwarded Only
- Disabled
NAT target - Defines the way NAT is implemented for the sake of Hairpinning. Masquerade is the default however this involves an additional lookup ad the mapping of done towards an interface. SNAT is faster (if ever measurable) as the NAT mapping point directly to the destination IP hence bypassing the lookup stage.
Multicast

Enable IGMP proxy - Runs the IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol) for your router.
LAN0/LAN1/LAN2/LAN3 - where enabled the bridges will partecipate in IGMP subscription using the router as a proxy between the LANs selected. This essentially allows IGMP to work between VLANs.
Enable quick leave - This is a feature of IGMP v2 and allows the router to stop streaming of the multicast IP as soon as the end device sends the quick leave IGMP packet.
Custom Configuration - This option allows you to set up some advanced parameters for the IGMP proxy daemon. Make sure to consult the official documentation.
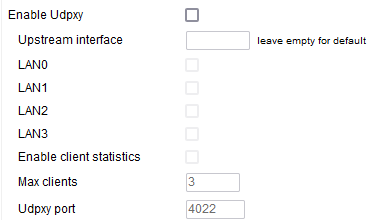
Enable Udpxy - Similarly to IGMP proxy Udpxy allows multicast communication between sender and receiver sitting in different VLANs. NOTE: since the behavior is pretty much identical you should use either but not both at the same time.
Upstream interface - leave empty for default - Defines where the stream source is expected to live.
LAN0/LAN1/LAN2/LAN3 - this is where the stream clients are expected to live.
Enable client statistics - As the option suggest if enabled statistical information about the clients is collected.
Max clients - Considering this is a lightwave protocol it works well for a limited number of clients, you might want to impose a maximum number if any.
Udpxy port- This is where you can consult the Udpxy information on your router.
Efficient Multicast Forwarding (IGMP Snooping) - IGMP snooping is a way to have the switch (router) facilitating the discovery of multicast (IGMP) clients. Beware that enabling IGMP snooping might interfere with some multicast-based applications/protocols. This issue is well-known, for example when using uPnP (Universal Plug 'n Play).
Force IGMPv2 - IGMPv2 enhances the IGMP communication supporting additional messages/behavior to optimise the end-to-end communication between client and server. Possibly the most important being the “Group Leave” message which is lacking instead in IGMP v1.