User Tools
Sidebar
Table of Contents
File sharing
In this menu, you can enable and configure Samba filesharing. Samba is a Linux clone of Microsoft's SMB (Server Message Block) filesharing protocol. Samba allows FreshTomato to “speak” the same language as Windows for file sharing across a LAN between Windows and Linux-based systems (such as FreshTomato). This allows you to use your router like a NAS drive, if you connect a USB storage device such as an external hard drive or flash drive.
Microsoft's SMB protocol was recently upgraded to v3. FreshTomato's implementation supports only v1/v2. However, these are fine for basic operations.
Samba File Sharing
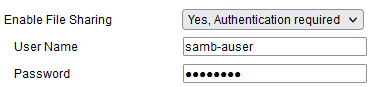
Enable File Sharing:
- No
- Yes, (with) no Authentication
- Yes Authentication Required
For a basic setup, select Yes no authentication. If you need additional security, it's recommended you select Yes, Authentication required. Doing so will display additional fields to set a single username and password.
Samba protocol version:
- SMBv1
- SMBv2
- SMBv1 + SMBv2
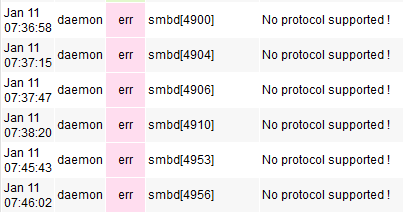
This lets you select the highest SMB version supported. It's good practice to enable both SMB1 and SMB2. Imposing a specific version can cause client devices running an incompatible version to be unsupported. This may generate log errors, such as the one seen below:
Disable GRO: Generic Receive Offload combines small packets to be sent as a one large one.
This optimizes network utilization, but involves extra reassembly. The default, (Enabled) disables GRO. Enabled is advised unless you have other requirements.
Workgroup Name: here, enter the Windows WORKGROUP name for PCs to be displayed/organized (for peer-to-peer network browsing).
Note that the Windows 10 April 2018 (v.1803) update eliminated Windows Homegroups. However, workgroups still exist in Windows 10/11.
Client Codepage: sets the Windows code page.
Windows clients use code pages to determine rules for mapping lowercase letters to uppercase ones. Undefined, by default, can be set in cases where case sensitivity is an issue. To check your Windows Codepage, run cmd.exe and type chcp to see the current code page.
Network Interfaces: here, define to which local interface samba will be bound. (Default: br0).
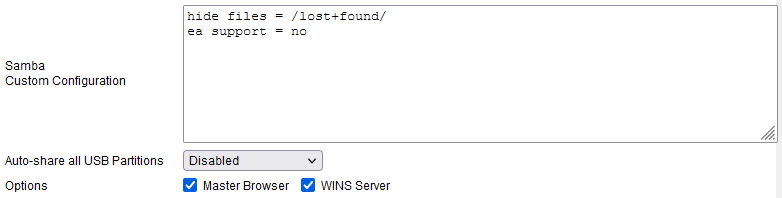
Samba Custom Configuration: here, specify user-defined settings for samba (written to “smb.conf”).
Consult samba documentation before using this field: https://www.samba.org/
Auto-share all USB Partitions: lets you configure automatic sharing.
As soon compatible USB filesystem storage is connected, its contents are shared.
- Disabled - automatic sharing will be disabled.
- Read Only - users can only open files and browse
the storage content. - Read-Write - users have full control of visible content.
- Hidden Read-Write - Read-Write privileges plus access to
hidden content (such as files starting with a period).
Options: configures Samba server to perform additional network roles:
- Master Browser - if enabled, participate in the Master Browser
election (when WINS is not available/defined). - WINS Server - if enabled, act as WINS server. DHCP clients will
receive the data via DHCP. Static clients can be set with FreshTomato's
LAN address as their WINS server setting.
Additional Share List
In this table, you can define custom network shares that map to physical filesystems. These may overlap, or even conflict with the Auto-share all Partition function described above.
Share name: The share name that appears under the [[\\WORKGROUP\$routerhostname]].
Directory: This defines where the share maps in the real filesystem.
Description: A descriptor only, that appears when browsing the network. It has no function except as a name.
Access Level: Specifies the network-level access rights
- Read Only
- Read-Write
Don't confuse this with filesystem rights. Total security is calculated by executing a logical AND operation on the Access Level rights and filesystem rights.
Hidden: A hidden share isn't visible when network browsing, but is available if called directly (say, by Windows' “net use” command).