User Tools
Sidebar
Wake on LAN
This function lets you a send a Wake-on-LAN signal (“magic packet”) to wired network devices to wake them/power them on. Wake-on-LAN is generally not supported by wireless devices.
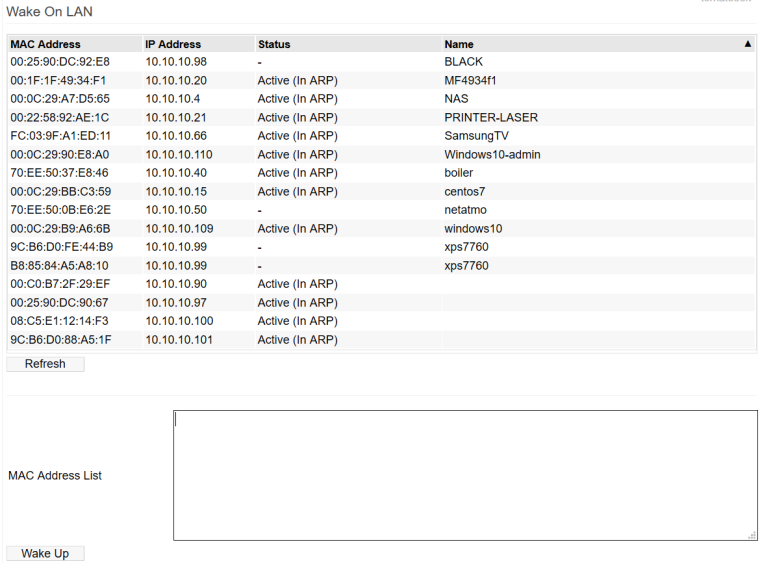
The list of devices on this menu includes:
- Devices already active in the ARP table.
- Devices defined in a DHCP Reservation/Static DHCP assignment.
- Devices defined manually in the Dnsmaq Custom configuration field
in the DHCP/DNS/TFTP menu.
For example:dhcp-host=70:EE:50:37:E8:46,myhostnamein
Some devices may appear with no defined hostname. You can define one in the Dnsmasq Custom configuration field as a workaround.
There are two ways to send a magic packet to a network device:
- Click anywhere in the list on the device to wake. The Wake Up
button briefly will grey out, then return. This indicates a magic packet
was just sent to that device's MAC address.
- Type the desired MAC addresses to wake into the MAC Address List box,
and then click Wake Up. Note that the Wake Up button also serves to save
the contents of the MAC Address List box for future use.
Wake on LAN Notes and Troubleshooting
For WoL to work, client devices must be configured to respond to magic packets, both in firmware and software. Enabling the firmware option causes the device's Ethernet chip to remain powered on even when the device is sleeping/off. This allows it to listen for magic packets. Enabling the software option allows the device to wake up/power on when that packet is received.
Most PCs have a Wake-on-LAN option to enable in UEFI/BIOS, named something like:
- Power on by PCI-E or PCI (Asus UEFI)
- PME Event Wakeup (AWARD BIOS)
- Power on by PCI devices (AMI BIOS)
You must also enable the WoL settings in your operating system.
For details, see:
HOWTOGEEK explains what is Wake on LAN and How Do I Enable it?
Microsoft Docs: WoL Behaviour in Windows 10
https://wiki.debian.org/WakeOnLan
