User Tools
Sidebar
Table of Contents
DHCP/DNS/TFTP
Here, you can configure advanced settings for the DHCP, DNS and TFTP services for both LAN and WAN. Most of this functionality is provided by dnsmasq.
DHCP Client (WAN)
The DHCP Client (WAN) section includes a dhcpc (dhcp client) options field. Here you can set parameters for your router's DHCP client.
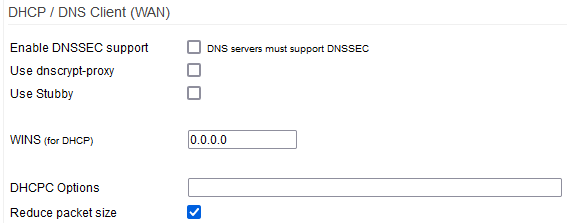
Enable DNSSEC support: enables support for DNS Security.
DNSSEC secures DNS by authenticating its servers. It prevents DNS hacking and poisoning. If the authoritative DNS server has DNSSEC, enabling it ensures DNS queries are answered by that DNS server, and not an imposter.
DNSSEC is compatible with standard DNS, as it isn't encrypted. Enable it for security if your DNS server supports it.
Use dnscrypt-proxy: enables DNSCrypt to encrypt DNS resolution.
When a DNSCrypt-enabled server is chosen, a unique key pair is generated every hour. Queries are then encrypted using this key pair before being sent to the server, usually on TCP port 443. The reply is also encrypted. Checking Use dnscrypt-proxy enables the built-in dnscrypt proxy client. Dnscrypt-proxy and Stubby cannot be used at the same time.
When dnscrypt-proxy is checked, the following options/fields appear:
- Ephemeral Keys - if checked, a new key pair is generated for each
DNS query. Use this with care, as it's very cpu-intensive, and may
slow DNS resolution.
- Manual Entry - if enabled, 3 more fields appear:
- Resolver Address - the IP of the dnscrypt-enabled DNS server.
- Provider Name - the DNS provider name, (e.g. “FreshTomato”).
- Provider Public Key - the public key from the DNSCRYPT-enabled
DNS provider (to generate a key pair)
- Resolver - a dropdown list of about 200 DNS servers.
- Some support DNSSEC.
- Some don't log queries.
- Some are filtered.
- Priority - should be left at no-resolv to prevent DNS leaks.
This should never be selected if DNSCRYPT is enabled.
To prevent leaks, enable Intercept DNS port.
- Local Port - the port on which dnscrypt-proxy speaks with
FreshTomato DNS. Leave this at 40 unless you're advanced.
Don't set it to 53, it could create a loop.
To help choose a DNSCrypt DNS provider, import the file /etc/dnscrypt-resolvers.csv in a spreadsheet. Once chosen,
the server's IP address, provider name, and public key can be taken from that file.
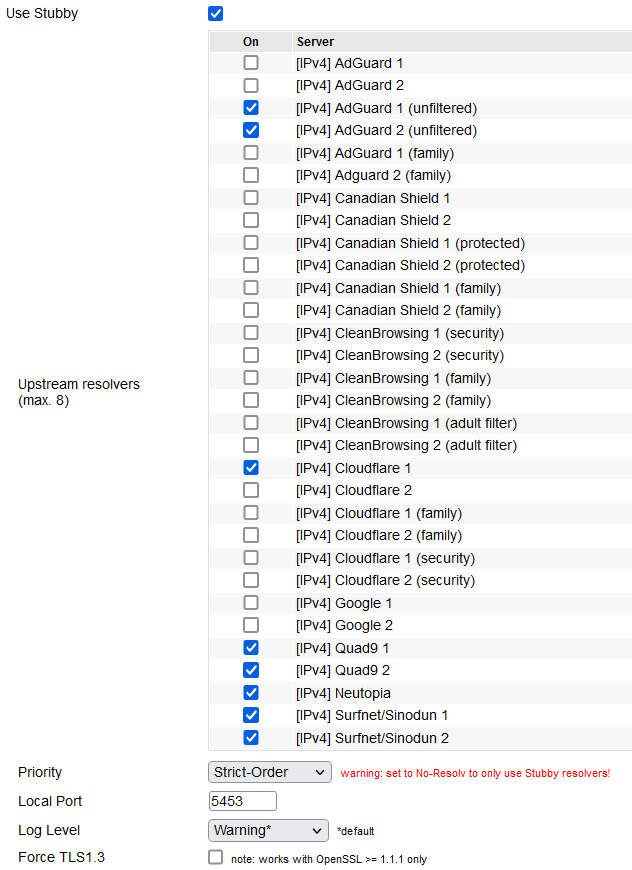
Use Stubby (DNS-over-TLS): enables the Stubby DNS Stub resolver, to enhance DNS privacy.
DNS over TLS (“DoT”) sends DNS queries via a secure (TLS-encrypted) connection. TLS is the same technology
that encrypts secure Web traffic. This prevents third parties from seeing your DNS queries.
- Show/Hide Servers: checking this displays a table of possible Stubby servers to be used.
Unchecking this hides the table.
Upstream resolvers: The actual list/table of possible upstream servers to use for performing name resolution.
Mousing over the name of any upstream resolver displays the following about about that server:
- The IP versions supported
- The server's status
- Authorized domain - (the domain name used for
authentication between your Stubby client and
an upstream DNS server that
supports encrypted queries. - The port used
Priority:
- Strict-Order - tries Stubby first. If issues arise, falls back
to resolution methods like standard DNS. - No-Resolv - if Stubby fails/has issues, there is no fallback
to other DNS resolution methods. - None - adds Stubby as a resolution method for dnsmasq.
This alone does not guarantee.
Local Port: the port Stubby uses to serve clients.
Dnsmasq will be the only client for Stubby, but serves the clients.
Log Level: here, choose what level of detail is written in log entries.
Force TLS1.3: enforces usage of TLS 1.3 for encryption. It must be supported upstream.
WINS (for DHCP): the IP address of a WINS Server to give to DHCP clients.
This doesn't enable WINS. WINS is enabled in the File Sharing menu. WINS is an old name resolution service to map NetBIOS names to IP addresses. It's mostly obsolete. DNS was supposed to replace WINS. However, WINS may still be necessary for some LAN browsing functions on old Windows versions.
DHCPC Options: in this field, enter custom configuration settings for the dhcp client.
Reduce Packet Size: reduces udhcpc discovery packet size for connection on ISPs with DHCP relays.
udhcpc (the DHCP client FreshTomato uses to obtain a WAN IP address) has a problem. It has a DHCP discovery packet size 590 bytes long. However, DHCP relay servers can handle only DHCP discovery packets up to 576 bytes. If there are DHCP relay servers between FreshTomato and your ISP's DHCP server, FreshTomato might fail to acquire a DHCP lease on the WAN interface.
The extra bytes were padding, and thus unnecessary. Developers deleted the padding, reducing udhcpc DHCP discovery packet size to 331 bytes. This size became the default setting. Now, udhcpc can successfully obtain a DHCP lease from an ISP with DHCP relays.
Some users may not be able to obtain a WAN IP address unless they disable this setting. (Default: Enabled).
DHCP / DNS Server (LAN)
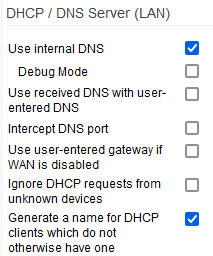
Use internal DNS: causes dnsmasq to be used as the LAN DNS server.
DHCP clients receive the router's LAN IP as the DNS server address. (Default: Enabled).
Debug mode: checking this makes FreshTomato write detailed information to the log file.
Use received DNS with user-entered DNS: adds DNS servers from the WAN's DHCP Server to the manual DNS server list.
See the Network menu for details. (Default: Disabled).
Intercept DNS port: causes DNS packets on port 53 to be redirected to FreshTomato's DNS server.
Only IPv4 DNS requests are intercepted. (Default: Disabled).
Use user-entered gateway if WAN is disabled: makes DHCP assign the router IP as the default gateway to LAN clients.
(Default: Disabled)
Ignore DHCP requests from unknown devices: makes dnsmasq ignore DHCP requests from MAC addresses not in DHCP Reservation.
These clients won't get an address via DHCP. The setting is also in the DHCP Reservation menu. (Default: Disabled).
Generate a name for DHCP clients which do not otherwise have one: if FreshTomato can't find a hostname for a client's DHCP/MAC combination, it generates one for display, based on its MAC address.
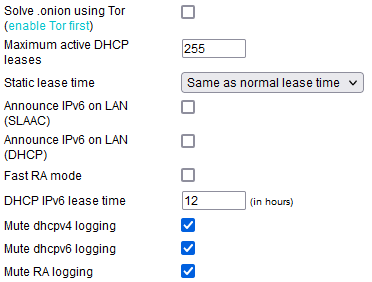
Solve .onion using Tor: if Tor is enabled, this makes it resolve “.onion” domains.
This allows proper DNS resolution on the Tor network. For details about the built-in Tor client, see the TOR page.
Maximum active DHCP leases: sets the maximum number of active DHCP leases at one time.
(Default: 255).
Static lease time: sets the absolute maximum valid time for any DHCP lease.
- Same as Normal Lease Time - static lease time is the same
as normal (1440 minute) lease time. (Default.) - Infinite - Static lease time is infinity
- Custom - lets you enter a custom Static DHCP lease time.
To retain leases after the router reboots, see this HOWTO for details on non-volatile DHCP leases.
Announce IPv6 on LAN (SLAAC): enables router advertisements for IPv6 (SLAAC) protocol.
SLAAC lets hosts self-configure an IPv6 address with minimal server contact.
- The client sends out an RS (router solicitation) ICMP packet.
- The nearest router responds with an RA (router advertisement) packet.
- The client uses the IPv6 prefix from the RA packet as the first
64 bits of its address. It then derives the last 64 bits of its address
using the EUI-64 process or a randomization algorithm.
Announce IPv6 on LAN (DHCP): enables router advertisements using IPv6 DHCP.
Fast RA mode: forces dnsmasq to be always in frequent RA mode.
DHCP IPv6 lease time: this sets the default lease time for IPv6 DHCP leases.
Mute dhcpv4 logging: stops FreshTomato from logging IPv4 dhcp activity. (Default: Disabled).
Mute dhcpv6 logging: stops FreshTomato from logging IPv6 dhcp activity. (Default: Disabled).
Mute RA logging: prevents logging of Router Advertisement activity.
Prevent client auto DoH: enabling this prevents DoH communication.
Modern browsers have DNS Over HTTP(s). With DoH enabled, a browser can bypass the network's DNS server. Enabling this option helps Adblock-DNS Filtering work properly, since it relies on unencrypted DNS resolution.
Enable DNS Rebind protection: helps prevent DNS Rebind DNS resolution attcks.
Using this may have side effects. (Default: Enabled).
Forward local domain queries to the upstream DNS: forwards local domains to the router's upstream DNS server.
Avoid using this unless your LAN has a fully (publicly)-registered domain.
Enable multicast DNS: checking this enables an implementation of Avahi mDNS.
Avahi lets programs publish/discover services and hosts running on a LAN. Its zero-configuration service includes multicast service discovery via mDNS/DNS-SD. “Bonjour” (Mac OS X) and “Zeroconf” technologies are Avahi-compatible.
Enable reflector: enables the Avahi mDNS repeater mode.
This makes Avahi re-transmit / re-multicast queries and responses via multiple interfaces. This allows the router to bridge multicast DNS networks.
For details, see this tutorial: Tomato Forum: avahi tutorial configuring a reflector aka mdns repeater
Custom configuration: here, you can add custom options to the dnsmasq configuration.
TFTP Server
Enable TFTP: starts dnsmasq's TFTP server with the “–tftp-no-fail” option enabled by default.
This prevents dnsmasq issues, for example, if TFTP root becomes unavailable.
TFTP root path: text here defines where TFTP root is located in the filesystem.
PXE on LANx (brx): enables Pre Boot eXecution Environment on the bridge(s).
PXE was designed for diskless clients. A PXE client can obtain an IP address via DHCP, then download boot code via a TFTP source. Syslinux is an example of this.
DHCP/DNS/TFTP Notes
Do not use results from Cloudflare's site: https://1.1.1.1/help. That webpage is likely to provide invalid results.
Instead, use: https://rootcanary.org/test.html
DNSSEC and DNSCrypt / Stubby complement each other.
- DNSSEC provides authentication.
- DNSCrypt provides encryption.
Custom stubby configuration
You can create your own custom stubby configuration. The stubby configuration generated via the web interface is located at: “/etc/stubby/stubby.yml”. You can use that as a template and replace the resolvers with the ones you want and save it in the “/opt” or jffs partition (assuming one is set up). Your custom config must be placed in: “/etc/stubby/stubby_alt.yml”. It will be used automatically when the service starts.
For example, the code below shows a custom configuration with NextDNS resolvers that is copied from the “/opt” usb partition as part of a wanup script.
Code:
cp /opt/usr/my_cool_stubby_config.yml /etc/stubby/stubby_alt.yml service stubby restart