User Tools
Sidebar
Table of Contents
FTP Server
The built-in File Transfer Protocol Server is an alternative way to transfer files to/from your router and its attached storage. This menu contains settings to configure that server. It's divided into sections including: FTP Server Configuration, Directories, Limits, Custom Configuration and User Accounts.
Before using FTP, you may want to consider the pros and cons of using it versus the NFS Server (in a *nix environment) or File Sharing via Samba. There are significant differences between them. In particular, FTP throughput can be much slower than either of the above.
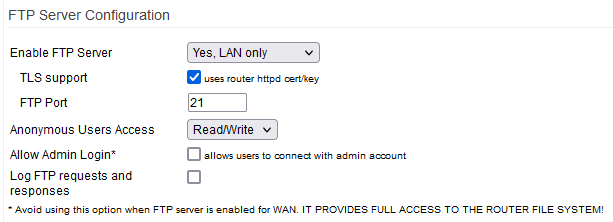
FTP Server Configuration
Enable FTP Server:
- No - the FTP Server is disabled.
- Yes - the FTP Server is enabled for WAN and LAN users.
- Yes, LAN only - the FTP Server is enabled only for LAN users.
TLS support: checking this enables support for TLS-encrypted FTP communications.
FTP Port: here, specify the port to use for communications. (Default: TCP 21)
Anonymous User Access:
Here, choose whether anonymous users can access the FTP Server and which file rights they're given.
- Disabled - anonymous users are not given access.
- Read Write - anonymous users are given read/write access.
- Read Only - anonymous users are given read access only.
- Write Only - anonymous users are given write access only.
Allow Admin Login: enables your local system administrator account as an FTP user.
Log FTP requests and responses: the FTP Server/syslog will log all FTP activity to “/var/log/messages”
This includes:
- Logons
- Logoffs
- Uploads
- Downloads
Directories
Anonymous Root Directory: specifies the filesystem location visible to anonymous users.
Public Root Directory: specifies the filesystem location accessible to any defined FTP user.
Private Root Directory: a filesystem location accessible only to the owner.
Each user has a protected subfolder in this location.
Directory Listings: this setting controls users' ability to do directory listings.
- Enabled - users are permitted to do directory listings.
- Disabled - users are not permitted to perform listings.
- Disabled for Anonymous - anonymous users aren't allowed to do directory listings.
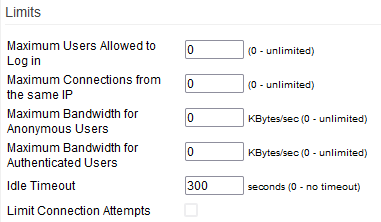
Limits
Maximum Users Allowed to Log in: sets the maximum number of logged-in users at once. Users above the limit are rejected.
Maximum Connections from the same IP: sets how many simultaneous connections are allowed for each user.
This is significant because an FTP user can log on via multiple sessions from the same address.
Maximum Bandwidth for Anonymous Users: FTP throttling limits available bandwidth to this value for each anonymous user.
Maximum Bandwidth for Authenticated Users: FTP throttling limits each authenticated user's bandwidth to this value.
Idle Timeout: specifies the timeout period, (seconds), until an inactive user is disconnected.
Limit Connection Attempts: if enabled, connection attempts beyond a maximum value are rejected.
Fields appear to enter the maximum number of logon attempts in a given time. This works when FTP is enabled on the WAN.
Custom Configuration
Custom configuration: here you can enter advanced settings. The underlying FTP Server is Vsftpd.
Consult official documentation before using this field. vsftpd
User accounts
Here, define FTP user accounts. Accounts defined here are given only FTP service rights. No Linux accounts are created.
Username: here, enter the ftp user account name.
Password: here, enter the ftp user account password.
Access:
- Read/Write - the FTP user is given read and write access.
- Read Only - the FTP user is given only read access.
- View Only - the FTP user is allowed only to view directory contents.
Read/Write: choosing this gives the user full access.
Read only: choosing this allows the user only to browse and download.
View Only: selecting this will mean the user can only browse directories.
Private: allows the user to access only their own folder (not the public area).