User Tools
Sidebar
Table of Contents
Adblock (DNS filtering)
This menu contains settings to configure FreshTomato's ad blocker-DNS filtering. This feature can block ads, some malware, crypto miners, privacy-invading scripts and more, depending on the lists you use.
You are strongly advised to read the How Adblock Works section to understand its functioning.
In documentation, the function/menu will be spelled capitalized (“Adblock”). The actual script will be spelled “adblock”, in lower case.
v1 and v2
There are currently two versions of Adblock: adblock_v1 and adblock_v2.
This table lists the Adblock versions available on different types of hardware
Adblock v1 functionality is taken from ad-blocking scripts outside FreshTomato. Do not enable one of those scripts and FreshTomato Adblock at the same time. Doing so may cause conflicts.
Adblock v2 uses advanced methods to block ads. It should be the preferred choice whenever possible.
How Adblock Works
Adblock works through DNS cache poisoning, as follows:
- A client makes a DNS request to resolve a (sub)domain.
- Dnsmasq searches both its positive lookup cache and its negative
lookup cache for a match of the requested (sub)domain. 1)
If it finds an entry, the script proceeds to step 5. If not, it proceeds
to step 3.
- Dnsmasq searches its configuration files for a corresponding
entry.
For adblock, the “dnsmasq.adblock” file holds the (sub)domains
to block. If an entry is found, it processes the entry. In the case
of adblock, the action is: resolve the domain to “0.0.0.0” or
“NXDOMAIN” (non-existent domain). Dnsmasq then proceeds
to step 5.
- Dnsmasq queries an upstream DNS server for the (sub)domain, directly
or via stubby/dnscrypt. The result is a positive lookup, or an
“NXDOMAIN”.
- The result from these steps is sent to the cache and returned
to the requesting client.
Given a source list, the original script just blocks ads. However, there are other reasons for your network to avoid communication with certain servers. Thus, the function was renamed “Adblock-DNS Filtering” to reflect increased abilities.
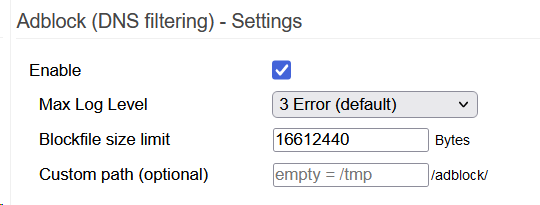
Adblock Settings
Enable: Checking this box turns on Adblock.
The adblock script downloads URL/domain lists to block, mostly from the Blacklist URL & Group-of-lists table. You can select/deselect any list in this table include in the downloads (the “blocklist”).
Debug mode (v1 only)
This enables debug mode for dnsmasq in the log. It tells FreshTomato to log all DNS queries routed to dnsmasq to the system log.
This is useful when testing/troubleshooting Adblock. Since this option was identical to “Debug Mode” in the DHCP/DNS/TFTP menu, it was removed from the Adblock menu in v2.
For more on testing, see the Notes and Troubleshooting section of this page.
Max Log Level (v2):
The newer v2 interface lets you set the maximum log level output the script will generate.
Options include:
- 0: The script will log only basic messages like start and stop.
- 3: (Error). Once you're confident with your setup, this option is sufficient. (Default).
- 4: Warning
- 5: Notification
- 6: Info
- 7: (Debug level) writes very detailed log information, useful for troubleshooting.
The higher the number, the more detailed the information the logs will record.
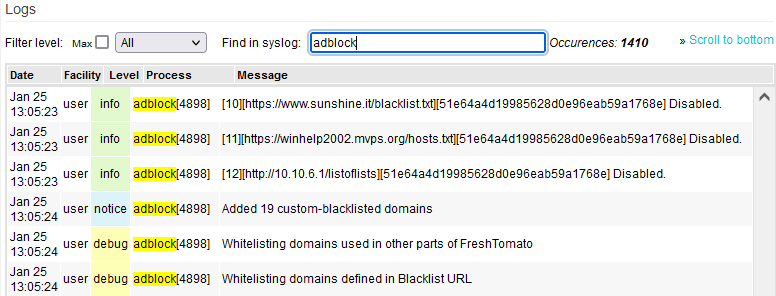
A good way to view Adblock log entries is to go to the Logs menu and type: “adblock” in the “Find in syslog” field. This filters the view to show only adblock entries.
When set to level 7, adblock writes additional debug files in: “/tmp/adblock.debug.$now,
(where “$now” is the absolute number of seconds passed). Adblock references in the the trace file are then displayed in the web interface.
Blockfile size limit (v2 only):
V1 may crash FreshTomato if it loads lists whose combined information exceeds the router's resource capacity. This can be hard to troubleshoot. Adblock v2 comes with a customizable ”limit“ field. If left empty, FreshTomato will calculate its value automatically. It will also calculate the value automatically if the router was reset to defaults.
When using external storage, the limit is calculated as 10% of physical RAM. When no external storage is found, the limit is calculated as 6.5% of RAM. The limit can be manually configured too. However, if the device becomes unstable, please revert to the auto-calculated value.
This is a limit, not a target. It's fine to have a smaller blockfile than the limit. A larger blockfile will result in longer restart times for the dnsmasq service. That's important because DHCP/DNS/TFTP won't function until dnsmasq finishes restarting. Since release 2026.2 the limit is now expressed in MB as opposite to Byte of the previous releases. This is entirely a visualization function under the bonnet calculations are still happening in Byte.
Custom Path (v2):
An important v2 option is the ability to configure a path to permanent storage. There, Adblock can store relevant files. Doing this is strongly encouraged. It allows extra script functionality. It allows Adblock to store whole lists, their http headers, and the compiled blockfile there. This offloads RAM demand (/tmp) to permanent storage, and lets information survive a reboot. It also makes troubleshooting easier.
It is also helpful when the script is rerun (manually or not) and there are no updated lists or configuration changes. The check for configuration changes involves controlling any modification to NVRAM variables since the last script run.
When a custom path is defined, Adblock will:
- Download all http headers from only the enabled lists.
- Compare those headers with the ones stored locally.
- Decide whether to re-process the blocklists or not.
This runs as follows:
- If the configuration did not change and;
- No updated lists are available;
- Skip the re-processing and return to idle.
This saves time and resources.
“Configuration”, in this case, is any externally-mapped files where blacklist_custom or whitelists are defined.
For example: ”/mnt/USB/my_whitelist.txt“.
Using a Custom path also allows adblock to load faster post-boot.
Domain Blacklist URLs & Group-of-Lists
This table contains a list of blacklists which can be downloaded and used to block ads.
On: Checking this makes Adblock enable downloading of the blacklist in that row.
Upon checking it, a gold star appears to confirm your choice. After selecting the blacklists to use, click Save.
Blacklist URL: shows the Internet location where that blacklist can be found.
Since r2023.4, the defaults don't include blocklists, to reduce NVRAM demand. You can add them manually. They are summarized on the official Adblock (DNS filtering) lists page.
Description: displays a name (if the publisher used one) or reference for the blacklist in that row.
Delete: if you move your mouse over a row with a blacklist, a red “x” shows at the end of the row. Clicking “x” deletes the row, and permanently deletes the blacklist.
There's no option to reset these to the original Blacklist URL entries.
If you delete an important URL, you will need to:
- Re-enter it into the Blacklist URL table or;
- Reset FreshTomato to default settings
However, the wiki contains a list of default blacklists: Adblock (DNS filtering) lists for your reference.
Add: inserts a blank row. There, you can type a new URL from which to download and use an additional Blacklist URL.
You can add a comment in the Description field.
Compatible data formats
Lists to download must be in plain text. V2 can extract domains from lists in several formats. Essentially, it uses a regex against each line in the file.
- Lines from the source file are parsed.
- Comments are removed.
- The domains are extracted.
This is true regardless of where (in which column) those domains are in the list.
Group-of-lists
V2 also accepts a new list format called “Group-of-lists”. This involves feeding the script a URL of links to a list of further URLs. The Group-of-lists is great at saving NVRAM space.
This can be visualized as follows:
URL |--> list
or:
URL |--> Group-of-lists-file |--> URL |--> list
|--> URL |--> List
|--> URL |--> List
|--> URL |--> List
A limitation of the Group-of-lists format is that it doesn't check the lists to assess whether they need downloading or not.
When needed, adblock automatically handles EOL (End of Line) characters in files by converting them internally.
Group-of-lists are visible in the log.
For example, if you see: ”[8][2]“ it would mean:
adblock is processing the 8th defined list in the Domain blacklist URLs & Group-of-lists on the second line (URL).
Domain blacklist custom
Domain Syntax
The syntax for this list is as follows:
- Standard domains (one entry per line).
- A ”#“ or ”!“ preceding text marks the line as comment only-
to be ignored by script. - A domain prefixed with ”+“ blacklists the domain
and prunes subdomains
found in the final blockfile.
This table summarizes the Domain blacklist syntax:
| Adding custom entry | Will blacklist / Do the following |
|---|---|
| sub.domain.com | sub.domain.com “sub2.sub.domain.com” and all subdomains of “sub.domain.com” |
| +sub.domain.com | sub.domain.com Will also prune blockfile of dupes/redundant entries. This reduces RAM usage, CPU cycles and storage space |
| # or ! | Any string defined before them is considered but the rest of the line is ignored. |
You can also specify a path to a domain file (one domain per line).
For example: ”/mnt/usb/blacklist.txt“.
Using external storage is convenient and offers some advantages for maintaining your blocklist. For example, moving a blacklist to another router would be as simple as removing a USB flash drive from one router and inserting it into the other (assuming both were set with the same storage location setting). Do not store blacklist-custom mapped files in the same location defined in Custom path, as the latter gets wiped periodically.
Sort a-z ↓ : introduced in r2024.1, this sorts the field contents alphabetically.
Domain whitelist
Domain whitelist syntax
The Domain whitelist can use:
- Standard domains (one entry per line).
- Prepending a ”%“ sign before an entry indicates a “strict” whitelisting.
Whitelisting always takes precedence over blacklisting.
For example, if a blacklist contained “ads.example.com”, whitelisting
“example.com” will undo the blacklisting of “ads.example.com”
and all other subdomains. - Prepending a ”#“ or ”!“ before an entry marks it as comment only-
it will be ignored by Adblock.
This table summarizes the Domain whitelist syntax:
| Adding custom entry | Will whitelist / Do the following |
|---|---|
| sub.domain.com | sub.domain.com sub2.sub.domain.com and all other subdomains of sub.domain.com |
| %sub.domain.com | sub.domain.com but not subdomains of sub.domain.com. Will also prune blockfile of dupes/redundant entries. This reduces RAM usage, CPU cycles and storage space. |
| # or ! | Any string defined before them is considered, but the rest of the line is ignored. |
You can also specify a path to a file of domains (one domain per line).
For example: ”/mnt/usb/whitelist.txt“.
Using external storage is both convenient and offers certain advantages for maintaining the blocklist. For example, moving a whitelist to another router would be as simple as removing a USB flash drive from one router and inserting it into the other (assuming both were set with the same storage location setting). Do not store you whitelist mapped file/s under the same location defined in Custom path as this latter gets wiped periodically.
Sort a-z ↓ : clicking this sorts the field contents alphabetically.
Maintaining the Domain whitelist
One way to maintain the whitelist is to share it on your LAN, and teach users nslookup verification and whitelist additions.
Such a process could be automated as follows:
- Map a file in the Whitelist section of the Adblock menu
- Share the file/folder via Samba, in the File Sharing menu
- Teach users:
- How to use nslookup on a URL to verify DNS lookups are being poisoned
- Where to find the whitelist (via its samba share) and;
- After the whitelist has been edited, to configure settings in Buttons/LED as follows:

With these settings, pressing the correct router button triggers the/usr/sbin/adblock updatefunction.
Update completion times vary. A swift run may take a few seconds. A full run might take minutes.
Enforcing Client Compliance
For Adblock to work properly, client devices must be configured with FreshTomato's IP address (dnsmasq) as their DNS server. This is done by configuring a static IP address on the client device itself or through FreshTomato's DHCP Service.
For the latter, enable DHCP. Then, enable the DNS server, and select “Use internal DNS” in the DHCP/DNS/TFTP menu.
These steps are mandatory. Clients that bypass FreshTomato's DNS server won't have their ads blocked.
Three optional settings improve Adblock operation:
- Enable Intercept DNS port in the DHCP/DNS/TFTP menu.
- Enable Prevent Client auto DoH in DHCP/DNS/TFTP.
- Enable the “DoH Server” list in Adblock to prevent DoH requests
from being resolved. The default DoH Server list since 2021.6
can be found at: oneoffdallas: DoH Server List
V1 functionality is a version of scripts from outside FreshTomato. Don't enable both an outside script and FreshTomato Adblock at the same time. It may cause conflicts.
Adblock v2 uses advanced methods to block ads. It should be the preferred choice whenever possible.
Adblock/DNS Filtering affects name resolution only. Adblock cannot block an application that communicates directly via IP address.
Thorough management of domain blocking can be tedious. For example, with email spam, you'll probably deal with false positives.
Regardless of version, the script is always named “adblock”, and can be found at: ”/usr/sbin/adblock“.
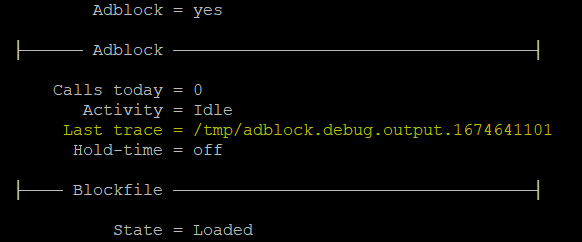
Adblock v2
Adblock v2 improves on the v1 script. It adds a richer feature set, increased user interaction (via toolbar) and command line options.
v2 Improvements
- Filters DNS like v1, but in a more precise, controlled way.
- Lets you run only certain functions to save time.
- Doesn't depend on list formats, as long as they're in plain text.
It just extracts domains from the different list types. - Can prevent resource issues. It assesses blocklist capacity before running.
It can self-diagnose/self-heal some basic resource problems.
For example: dnsmasq not running due to RAM shortage. - Supports Swift-run mode. You can add a domain to lists without having
to reprocess (download) whole lists again. - Supports external storage. Lists and headers can be stored there to
help decide which lists to download, reducing traffic/processing time. - Prevents false positives via a 30-minute interval between runs.
This enables after updates. - Includes more troubleshooting options, including debug logging and
script tracing. These can look into the lowest operating script levels. - Can be operated via web interface or command line.
To get help with adblock at a command line, type adblock help:


Further debugging files can be accessed at the command line by typing: adblock status:
To open the last trace file automatically, type adblock trace:

You'll be prompted to select the viewer in which to view trace files.
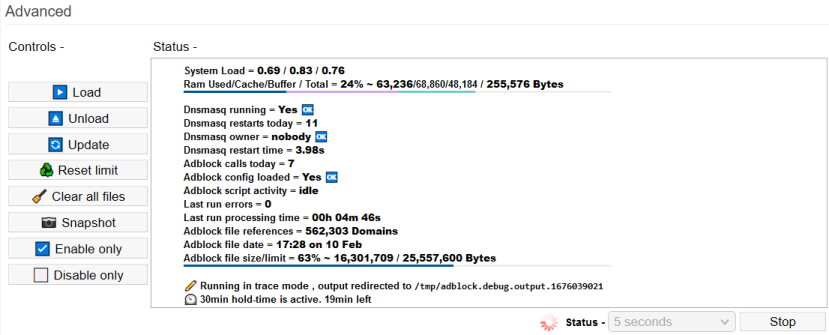
Using the v2 Controls
The Controls button bar in the Advanced section let you control adblock script execution.
Refresh: A new command at the table bottom. Refreshes are limited to a minimum frequency of 5 seconds. Refreshing more often makes the system load climb.
Swift-run (v2) and Full-run (v1) Operations
Modifications to the adblock script configuration are categorized as follows:
- List (enable/disable)
- List content update
- Change of parameters (loglevel / blockfile limit / path )
- Addition of a simple blacklist_custom
- Addition of a simple whitelist
- Addition of pruning blacklist_custom
- Addition of a strict whitelist
- Removal of a blacklist_custom
- Removal of a whitelist
Only two operations from the above list that can be run in Swift-run mode:
- No. 4 - Addition of simple custom blacklist domains and;
- No. 5 - Addition of simple whitelisted domains
This is because they don't require full processing.
These are the most common operations performed when maintaining adblock script settings. Swift-run operations are performed live on a running blockfile. Therefore, the adblock script must be loaded in order to run functions (4) or (5). A swift run can be completed in seconds. A full run may take minutes. All operations other than (4) or (5) require a full run.
“Swift” is a temporary action to allow your change to become immediately functional. In contrast, a successive full run (manual or not) processes added domains in the standard way.
Command line operations (v2)
Another new v2 feature is the ability to interact with adblock at the command line.
As seen above in this “adblock help” screenshot, v2 has many more functions available:
The table below summarizes all command switches (v2 only):
| Command switch | Type the following | Performs the following task/Comments. |
|---|---|---|
| Help | “adblock help” | Displays a summary guide of valid commands. |
| Status | “adblock status” | Gives constant updates on adblock's operational status. |
| Start | “adblock start” | The same as “Load” in the Web interface. |
| Stop | “adblock stop” | The same as “Unload” in the Web interface |
| Update | “adblock update” | The same as “Update” in the Web interface. |
| Upgrade | “adblock upgrade” | Checks online for script upgrades. If one is available, it prompts you to install the upgrade. This downloads the latest script version into /tmp (RAM) then mounts it over the built-in version. Since the script is stored in RAM, it will be lost after a reboot. Thus, an extra parameter is supported: “adblock upgrade silent”. If an upgrade is available, this triggers it without prompting you. This may be used in the init script, to ensure the latest version runs, even after a reboot. |
| Test | “adblock test $domain” | Does a quick test to check a domain name is being blocked. Helpful when troubleshooting. |
| Reset | “adblock reset” | The same as “Reset” in the web interface. |
| Clear | “adblock clear” | The same as “Clear all files” in the web interface. Resets the blockfile maximum limit. |
| Trace/Status | “adblock trace” | Only available at the command line. When the script is run with Loglevel set at 7, adblock runs in “trace mode”. Every command executed by the script is saved into a trace (log/debug) file. Find the trace file using “adblock status”. Running “adblock trace” will open the latest appropriate trace file even more easily. |
| Snapshot | “adblock snapshot” | The same as “Snapshot” in the web interface. |
| Enable | “adblock enable” | The same as “Enable” in the web interface. |
| Disable | “adblock disable” | The same as “Disable” in the web interface. |
Adblock test command (v2)
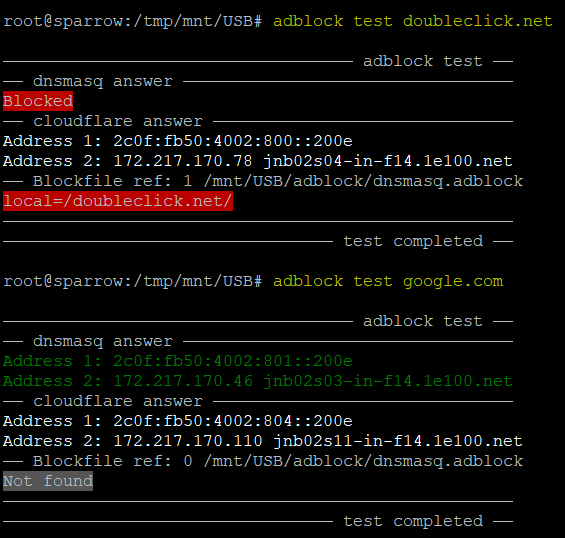
For quick and easy testing of broken resolution or other DNS issues, use the “test” switch.
Typing: “adblock test example.com” will quickly test whether name resolution is functioning.
Specifically:
- Dnsmasq answer - Displays the actual name resolution as seen
by the router and LAN users.
The word “Blocked” is displayed if access to the domain was blocked. - Cloudflare answer - This query bypasses the usual dnsmasq process
and sends a query to address 1.1.1.1 .
This can help verify if a domain exists. - Blockfile ref - Checks the blockfile for references to the tested domain.
With these 3 pieces of information, it's easy to assess whether a domain is blocked, non-existent, or intact.
Automatic list updates
Normally, adblock adds a crontable entry to perform a daily list update. Now, update times are randomized to avoid DDoS of the list providers' servers. a A new update time is set each time you run adblock stop or reboot. The update's time window varies between 02:00 AM and 05:59 AM local time, depending on the script version run.
To verify the current scheduled update time, type:
root@router:/# cru l | grep adblockJob
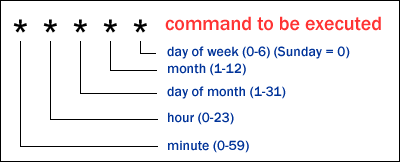
28 4 * * * /usr/sbin/adblock update #adblockJob#
In this example, the output is 28 (min) 4 (am) * (Every day) * (Every month) * (All days of the week).
The image below illustrates the syntax of crontable expressions:
For help automating/verifying correct crontable expressions, see: crontab.guru
If you stop adblock, the crontable expression is removed. This is by design.
Future development goals
- Add an option to let FreshTomato users share their Whitelists.
This would allow creation of a shared database of “good” domains,
based on user experience.
This shared whitelist would be downloaded the same way
you would download any blacklist. - Add a test function to the web interface (currently only via CLI).
Adblock Notes and Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting v1
You can test Blacklisted or Custom entries by using the nslookup tool (Windows/Linux/MacOS). Simply run nslookup and enter the domain/URL to be tested. If it resolves to 0.0.0.0, then Adblock is working properly, and the domain is being blocked. You can also check FreshTomato's System log (Syslog) to see if Adblock activity is reflected there.
For example, this entry shows that dnsmasq replaced the true IP address of hbx.media.net with 0.0.0.0.
Jan 9 19:57:29 rt-n66 daemon.info dnsmasq[4872]: config hbx.media.net is 0.0.0.0
Adblock worked properly.
Crashing
If your router crashes, you may be using too many large Blacklists, which can exhaust available RAM. Try using smaller blacklists, or fewer large ones. Adblock v2 is much less likely to exhaust RAM.
Websites for Testing
Some websites allow you to test the effectiveness of your Adblock configuration. When using them, ensure you don't have adblock/script-block plugins enabled in your browser or your results will be invalid.
Some good adblock testing sites include:
Adblock won't work with DoH, DoT and other Encrypted DNS lookups
Increasingly, devices use DNSSEC, and encrypted DNS protocols, such as DoH [DNS over HTTP(S)]. Adblock won't work with these lookup methods. This is because if lookup requests are encrypted or directed to a third-party server, Adblock can't intercept, and therefore can't poison them.
Enabling the “DoH Server” blacklist in the Blacklist URL table may help with this. It will download, then block access to common DoH servers.
Troubleshooting v2
When troubleshooting, it's best to set the loglevel at 7, (as described in the Settings section above). Then, analyze the logs and trace file. Often the list publishers suffer from issues such as downtime, or a broken cache. It's common to see adblock fail to download a list one day but download it the next day without issue.
In order to learn what might be wrong, you should understand adblock's status indicators.
Here are a few signs which may indicate a problem:
- System load is too high in the 5min+ section (For example, > 1.5)
- RAM usage is too high (> 90%)
- Dnsmasq ownership remains root (non-operational) until lists are fully loaded.
It's normal to see “root” briefly, but this should switch to “nobody” within 20 seconds. - Too many dnsmasq restarts
- Dnsmasq restart time is too high (> 15 seconds)
- Adblock calls today
- Last run errors
If the Blockfile size exceeds the Blockfile size limit value, the file size will be reduced. If (with limit manually set high) dnsmasq still doesn't run properly afterwards, the safeDnsmasqRestart() process will reduce the Blockfile size in increments of 5%. After each reduction, it will reattempt to fully start dnsmasq. When dnsmasq functions properly, the new auto-calculated limit is set as the current Blockfile size limit.
When a trace is running, FreshTomato will display this (FIX ME!) in the Web interface:

The additional debugging files can also be accessed at the command line by typing: adblock status
To open the last trace file automatically, type adblock trace at a command shell. You'll be prompted to select the viewer in which to view trace files.
Apple iOS devices (iCloud paid service only)
iOS devices have settings which may interfere with Adblock operation. “Limit Address Tracking”
can be disabled on a per-WLAN basis, seen here:
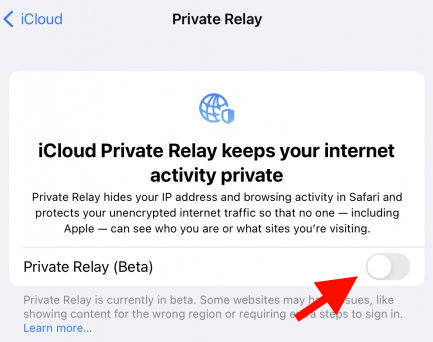
Alternatively, you can disable it globally via the “Private Relay” setting, seen below:
You might connect your mobile/laptop to different WiFi networks at different locations. For this reason, it makes sense to disable Private Relay on a per-WLAN basis. It is wise to disable it wherever FreshTomato provides your Internet connection and Adblock is enabled.
Remember, these options are only available to paid iCloud customers.